Name
Chamberlain University
BIOS-242 Fundamentals of Microbiology
Prof. Name
Date
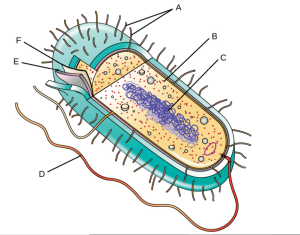
• Draw an image of a Prokaryotic cell in the space below. Label all the organelles and structures present in a typical prokaryotic cell. A. Fimbriae B. Ribosome C. Nucleoid D. Flagellum E. Cell Wall F. Plasma Membrane
• Complete the following table by listing various organelles and structures commonly found in a Prokaryotic cell and describe their functions in 1-2 sentences.
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. There are two primary types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are generally simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and contain distinct membrane-bound structures.
In a typical prokaryotic cell, several organelles and structures serve specific functions essential for the cell’s survival. For instance, the capsule protects the cell from being engulfed by other organisms, while the cell wall provides the cell with shape and protection. Pili enable the cell to attach to other bacterial cells, and the flagella aid in locomotion. Plasmids are circular DNA structures that carry genes not involved in reproduction. Ribosomes, responsible for protein production, and the cell membrane, which regulates the flow of substances in and out of the cell, are also present in prokaryotic cells. The cytoplasm, composed mainly of water, contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules, while the nucleoid region houses the bacterial DNA.
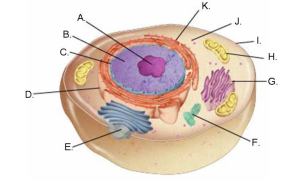
Similarly, eukaryotic cells contain several organelles, each performing specific tasks. The cytoplasm is the material between the cell membrane and the nucleus. The cell wall supports and protects the cell, and the cell membrane serves as the boundary between the cell and its environment, regulating the entry and exit of materials. Mitochondria, the site of cellular respiration, convert food into ATP, while chloroplasts capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in plant cells. Vacuoles store materials, flagella are used for movement, and lysosomes contain enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. The nucleus stores DNA and controls most cellular processes, while ribosomes make proteins using instructions from the nucleus. The nucleolus is the region within the nucleus where protein assembly begins.